Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a powerful approach for retrieving information from documents, but it often struggles with multi-hop legal reasoning across multiple sources. In a recent proof-of-concept (POC) for a legal client, we implemented Graph RAG for legal reasoning—a hybrid system that converts text into triplet-based knowledge graphs, leverages graph traversal for multi-hop context assembly, and synthesizes responses with LLMs.
This article explores practical methodologies, emerging research trends (including Microsoft’s GraphRAG framework), lessons from migrating from proprietary to open-source models, and an enterprise-ready blueprint for deploying Graph RAG in production.
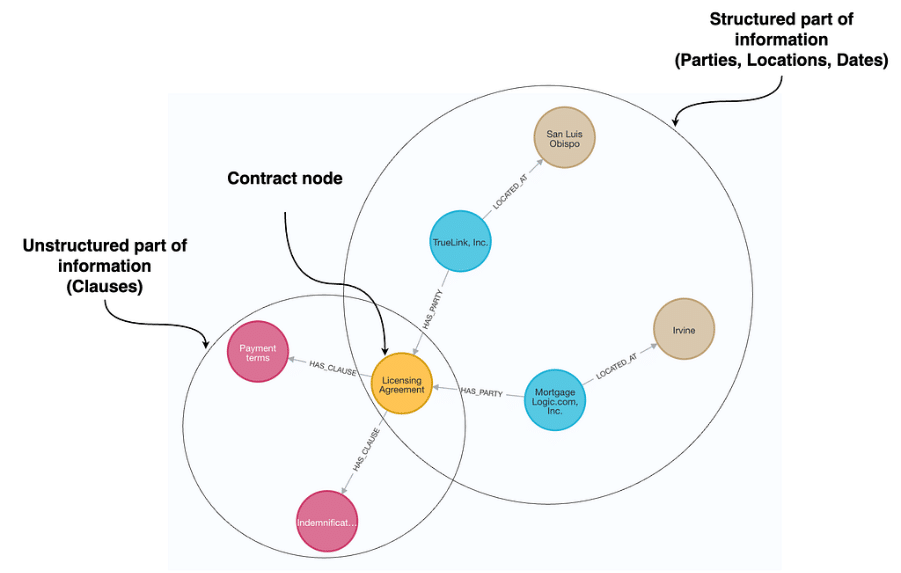
Source: https://cdn-images-
1.medium.com/max/1024/1*jmw9OfKkRD6SOI7uEusWGQ.png
Why Standard RAG Fails for Multi-Hop Legal Queries
Traditional RAG systems retrieve top-k text chunks via vector similarity for LLM processing. While effective for single-document queries, they often fail with complex legal questions like:
“Which statute defines ‘confidential information,’ how does it cross-reference data protection obligations, and what exceptions apply under recent amendments?”
Legal corpora scatter definitions, cross-references, citations, and commentary across multiple documents. Accurate answers require explicit entity-relation linking rather than relying on co-occurrence in one chunk. Benchmarks such as MultiHop-RAG and RobustQA report traditional RAG achieving only 32–75% accuracy on multi-hop tasks, whereas graph-enhanced approaches exceed 85% accuracy.
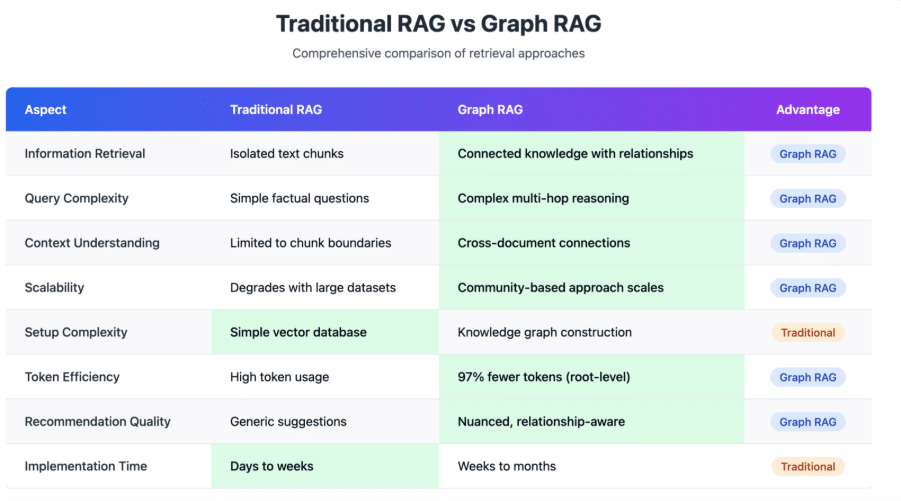
Source: mlwhiz.com
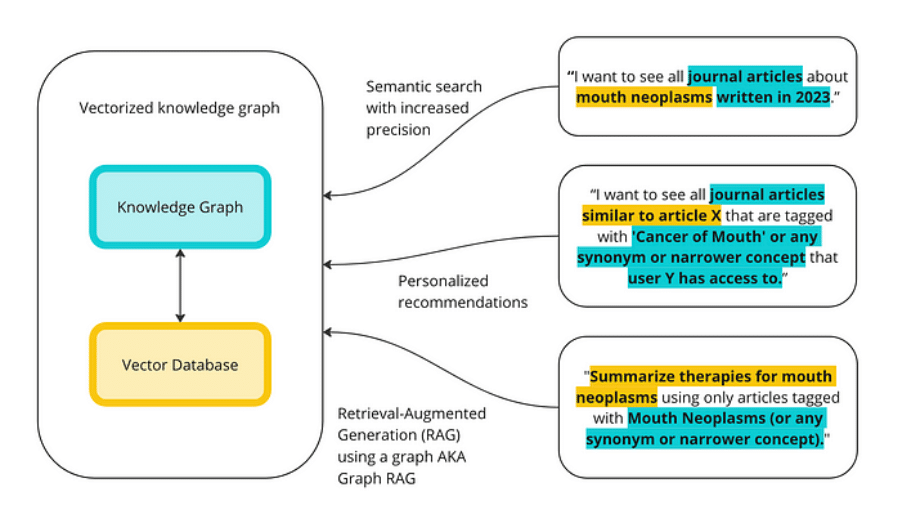
Research confirms that integrating knowledge graphs with RAG improves multi-hop reasoning, explainability, and hallucination reduction by providing structured, traceable paths.
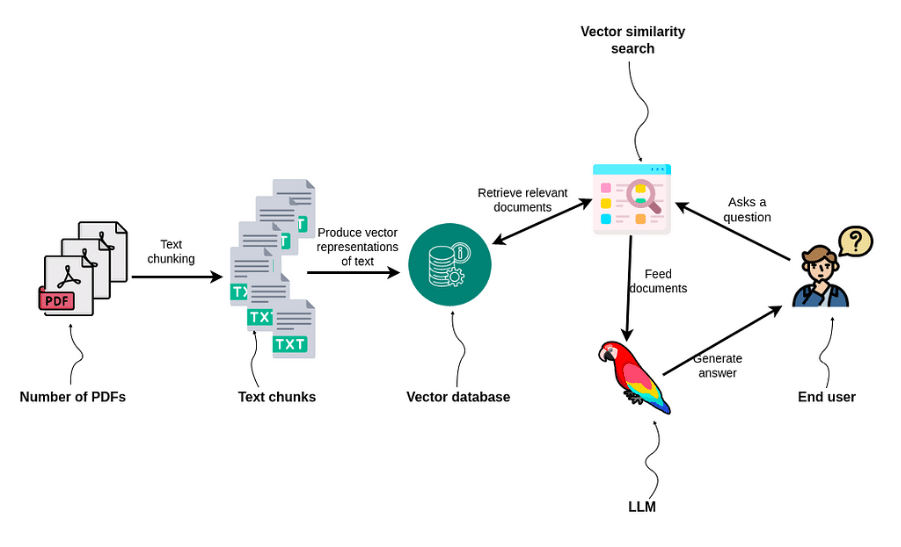
Source: neo4j.com
How to Improve Multi-Hop Reasoning With Knowledge Graphs and LLMs
Core Idea: Combining Vectors + Graphs + LLMs (Hybrid Retrieval)
Graph RAG is a hybrid retrieval framework addressing limitations of traditional RAG with three key components:
- Chunk & Embed Text (Vector Store) – Enables fast semantic matching for relevant content retrieval.
- Extract Entities & Relations → Triplets (Knowledge Graph Construction) – Converts documents into nodes (statutes, clauses, entities) and edges (defines, amends, cites, applies_to, exceptions).
- Graph Traversal → Assemble Multi-Hop Context – Builds structured multi-document subgraphs, often using techniques like community detection, hierarchical summarization, or leapfrog traversal.
This deterministic traversal (A → B → C) significantly outperforms probabilistic vector retrieval in interconnected legal data. For example, Microsoft’s GraphRAG pre-summarizes community hierarchies, yielding 20–70% better comprehensiveness on complex legal tasks. LLM and Knowledge Graph integration
Source: towardsdatascience.com
Recent implementations (Neo4j + LlamaIndex) demonstrate hybrid retrieval improving multi-hop query precision by 3x, enhancing auditability critical for legal applications.
POC Architecture: A Production-Oriented Blueprint
Our legal POC followed these steps:
- Ingestion & Chunking: Parse PDFs, split by clauses/sections, normalize citations and temporal metadata.
- Embedding & Vector Store: Generate embeddings per chunk (Qdrant used for hybrid capabilities).
- Knowledge Graph Store: Persist triplets in a scalable graph DB (NebulaGraph or Neo4j for traversal).
- Triplet Generation: LLM-driven pipeline for entity-relation extraction with canonicalization and provenance tagging.
- Query Planner: Decomposes queries into graph traversal intents with vector fallback.
- Answer Synthesis: Feeds annotated subgraphs to the LLM for reasoned responses with provenance.
Open-source libraries like LlamaIndex and LangChain integrate seamlessly with Qdrant + Neo4j/Nebula hybrids for Graph RAG. Explore more about our Enterprise AI solutions
Triplet Extraction: The Critical Challenge
Best practices for triplet extraction in legal knowledge graphs include:
- Entity Detection & Relation Classification: Use domain-specific prompts (e.g., “amends,” “revokes,” “cites”).
- Canonicalization & Deduplication: Normalize entities (e.g., “GDPR” → “Regulation (EU) 2016/679”).
- Provenance & Temporality: Tag sources and validity dates to handle evolving laws.
High-capacity LLMs (e.g., GPT-4) deliver superior triplet quality. Smaller models often introduce errors, breaking multi-hop reasoning chains. Hybrid approaches (LLM + rule-based extraction) provide robust results.
Cost vs Quality: OpenAI → Open-Source Migration Insights
Balancing cost and quality in LLM-driven KG extraction is key for scaling Graph RAG in enterprise legal applications. Our POC with 60+ legal documents revealed:
- Proprietary Stack (OpenAI embeddings + GPT-4o-mini): High-fidelity graphs, precise entity resolution, robust multi-hop answers. Recurring API costs are high when scaling to thousands of documents.
- Open-Source Stack (MiniLM + Qwen-family LLMs): Drastically reduced API costs, but lower triplet quality reduced multi-hop accuracy by 30–40%.
Practical takeaway: Use premium LLMs for initial KG construction and open-source or cached models for query serving and inference. This hybrid approach ensures both scalability and regulatory compliance.
Partner with 47Billion for Enterprise-Grade Graph RAG
At 47Billion, we provide end-to-end enterprise solutions in regulated domains like legal and compliance:
- Comprehensive Architecture: Ingestion → KG extraction → Hybrid retrieval → Orchestration.
- Validated Blueprints: Qdrant, Neo4j/Nebula, and cost-optimized LLM pipelines.
- Legal-Grade Features: Temporal graphs, audit trails, and regulatory alignment.
Explore scalable, explainable Graph RAG for multi-hop legal reasoning: 47Billion Solutions