Data-Driven Excellence: Crafting Seamless User Experiences
In today’s digital landscape, the fusion of data analytics with design has revolutionized how digital product interfaces engage with users. As we delve into this dynamic realm, it’s crucial to acknowledge the impact that data-driven approaches have had on shaping exceptional user experiences. Real-world statistics reveal a compelling narrative: companies leveraging data to drive their design decisions witness a staggering increase in conversion rates by up to 300% compared to their counterparts relying solely on intuition or assumptions.
Consider Spotify, a leading tech platform that epitomizes the application of data-driven design to enhance user experiences. Through its sophisticated algorithms analyzing user behavior, Spotify curates personalized playlists, Discover Weekly, Release Radar, and Daily Mixes, captivating users with over 60% of its listening attributed to personalized recommendations. This data-driven approach not only retains users but also amplifies user satisfaction by tailoring content precisely to individual preferences.
Moreover, the merits extend far beyond mere engagement metrics. Google, with its search engine interface continually evolving based on user behavior and intent, stands as another exemplar. Its search algorithms, updated over 500 times a year, prioritize user experience by delivering the most relevant results to billions of queries daily. This commitment to data-driven design is reflected in Google’s dominant 90% share of the global search engine market.
In this blog, we’ll understand the principles behind data-driven design, spotlighting its tangible benefits and unveiling how companies harness actionable insights to craft compelling experiences. Join us on this journey into the realm where data and design converge to sculpt captivating user experiences, transcending mere aesthetics to foster deeper connections and heightened functionality.
What is a data-driven design?
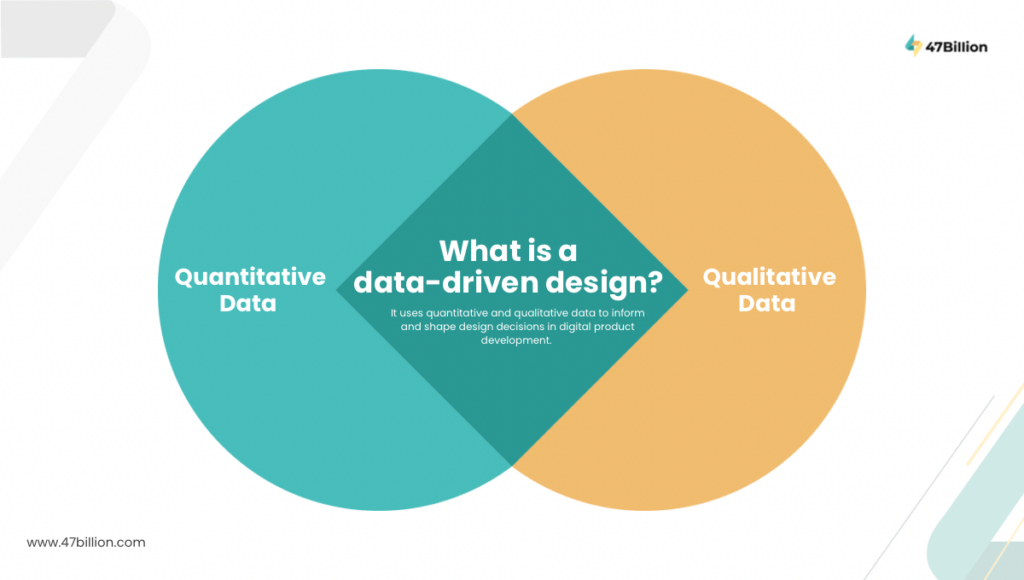
Data-driven design uses quantitative and qualitative data to inform and shape design decisions in digital product development. Designers use actual user behavior and preferences from user research to drive decision-making, creating more effective and user-centric solutions. This approach minimized assumptions and guesswork, resulting in targeted and relevant product design decisions. By incorporating data into the design process, designers can understand user needs and enhance user satisfaction, allowing them to balance user and business goals effectively.
Types of data for design
Quantitative Data
It is numerical and measurable, giving designers objective insights into user behavior and interactions. This quantifiable data type is valuable for identifying trends and patterns, allowing designers to make informed decisions based on hard evidence. For instance, a designer may analyze website analytics to determine which pages receive the most traffic or where users tend to drop off, guiding layout and content improvement decisions.
Qualitative Data
It is non-numerical and focuses on subjective user opinions, feelings, and motivations. This qualitative data helps designers understand the “why” behind user behavior, offering a deeper insight into user needs and expectations. For instance, conducting user interviews or analyzing reviews and feedback from usability testing can reveal user pain points and help inform the design process, leading to more user-centric solutions.
Important Data Sources for Designers
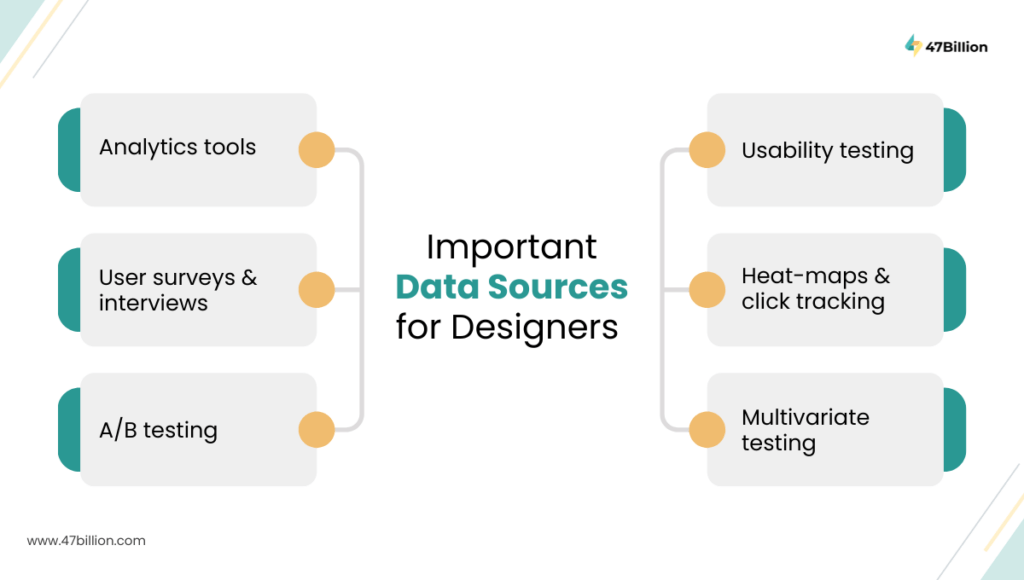
Here are six domains where design teams typically source data:
- Analytics tools
- User surveys & interviews
- A/B testing
- Usability testing
- Heatmaps & click tracking
- Multivariate testing
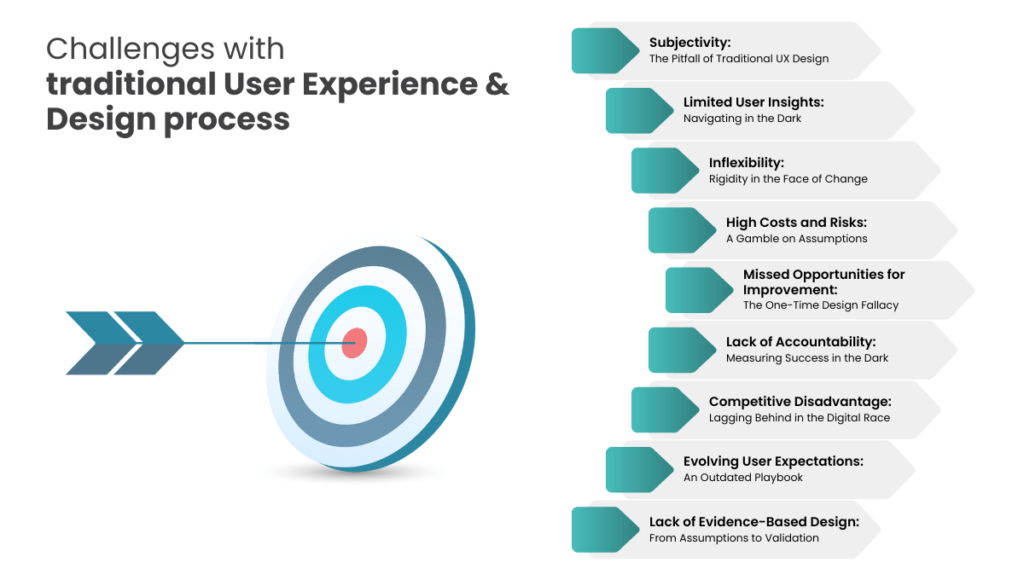
Challenges with traditional User experience and design process
The transition from traditional UX design to the dynamic realm of contemporary data-driven design wasn’t by chance; it emerged from intrinsic limitations that impeded the efficacy of conventional practices. Delving into these constraints provides a nuanced understanding of why the evolution was imperative.
In the legacy of traditional UX design, inherent shortcomings were glaring. Subjectivity permeated decision-making, relying heavily on designer and stakeholder opinions. This approach needed more depth of user insights, operating without comprehensive data and feedback. The rigidity of linear workflows hindered adaptability to evolving user needs and market dynamics, while the absence of data-driven decision-making elevated costs and risks.
Furthermore, the traditional model treated design as a static event, missing opportunities for continuous improvement. Accountability and measurability need to be improved, leaving success evaluation in the Dark. Faced with evolving user expectations and an ever-competitive landscape, traditional UX design found itself needing to be equipped to meet the demands of a dynamic digital age. The ascent of data-driven design represents a strategic response, a transformative solution addressing these limitations through empirical evidence, understanding user behavior, and iterative enhancements in tune with evolving expectations.
Subjectivity: The Pitfall of Traditional UX Design
Traditional UX design often relied on subjective decision-making, where the opinions and assumptions of designers and stakeholders shaped design choices. This subjectivity introduced a significant risk, leading to designs that might not align with actual user preferences or needs. The consequence is suboptimal user experiences that could have resonated with the intended audience.
Limited User Insights: Navigating in the Dark
Without access to comprehensive user data and feedback, traditional UX design works in the Dark. That is, the lack of deep insights into how users interacted with digital products made it challenging to make informed design choices. Designers were essentially guessing that resulted in products that might miss the mark in meeting user expectations and needs.
Inflexibility: Rigidity in the Face of Change
Traditional design processes often adhered to linear and inflexible workflows. This rigidity made it difficult to iterate and adapt to rapidly changing user needs and market conditions. The inability to create responsive and agile user experiences left traditional approaches trailing behind in a landscape that demanded adaptability.
High Costs and Risks: A Gamble on Assumptions
Relying solely on intuition and assumptions in traditional design practices posed significant financial and operational risks. High development costs, extended time-to-market, and an increased risk of project failure were expected outcomes. The absence of data-driven decision-making added burdens that businesses could ill-afford, especially in a competitive digital environment.
Missed Opportunities for Improvement: The One-Time Design Fallacy
Traditional UX design treated design as a one-time event, missing out on continuous improvement opportunities. This approach led to products and services that failed to evolve to meet changing user needs, continually missing chances to enhance the user experience over time.
Lack of Accountability: Measuring Success in the Dark
Traditional design approaches needed to have the accountability and measurability that data-driven methods brought to the table. Clear metrics and data were absent, making it challenging to evaluate the success of design decisions. The lack of tangible evidence hindered pinpointing areas that needed improvement or optimization.
Competitive Disadvantage: Lagging in the Digital Race
In an increasingly competitive digital landscape, businesses relying on traditional techniques need help to stand out and deliver superior user experiences. The inability to adapt quickly to user preferences put them at a disadvantage, with more agile competitors gaining an edge.
Evolving User Expectations: An Outdated Playbook
As technology advanced, user expectations evolved rapidly. Traditional UX design practices often found themselves playing catch-up. Users demanded more personalized, intuitive, and efficient digital experiences, necessitating a shift toward a data-driven delivery approach to stay relevant.
Lack of Evidence-Based Design: From Assumptions to Validation
Traditional UX design needed more empirical evidence to validate design choices. In contrast, data-driven design relies on empirical data and analytics to continuously validate and optimize designs. This shift from assumptions to evidence-based design is pivotal in creating digital experiences grounded in user behavior and preferences.
In response to these critical shortcomings, data-driven design emerged as a transformative solution. By leveraging data and analytics to inform design decisions, data-driven design addresses the limitations of traditional techniques. It brings empirical evidence to the forefront, understands user behavior, and enables iterative improvements that align with evolving user needs and expectations. Data-driven design has indeed become a cornerstone of modern UX design, offering businesses a more effective and user-centered approach to creating digital products and services in today’s dynamic and competitive landscape.
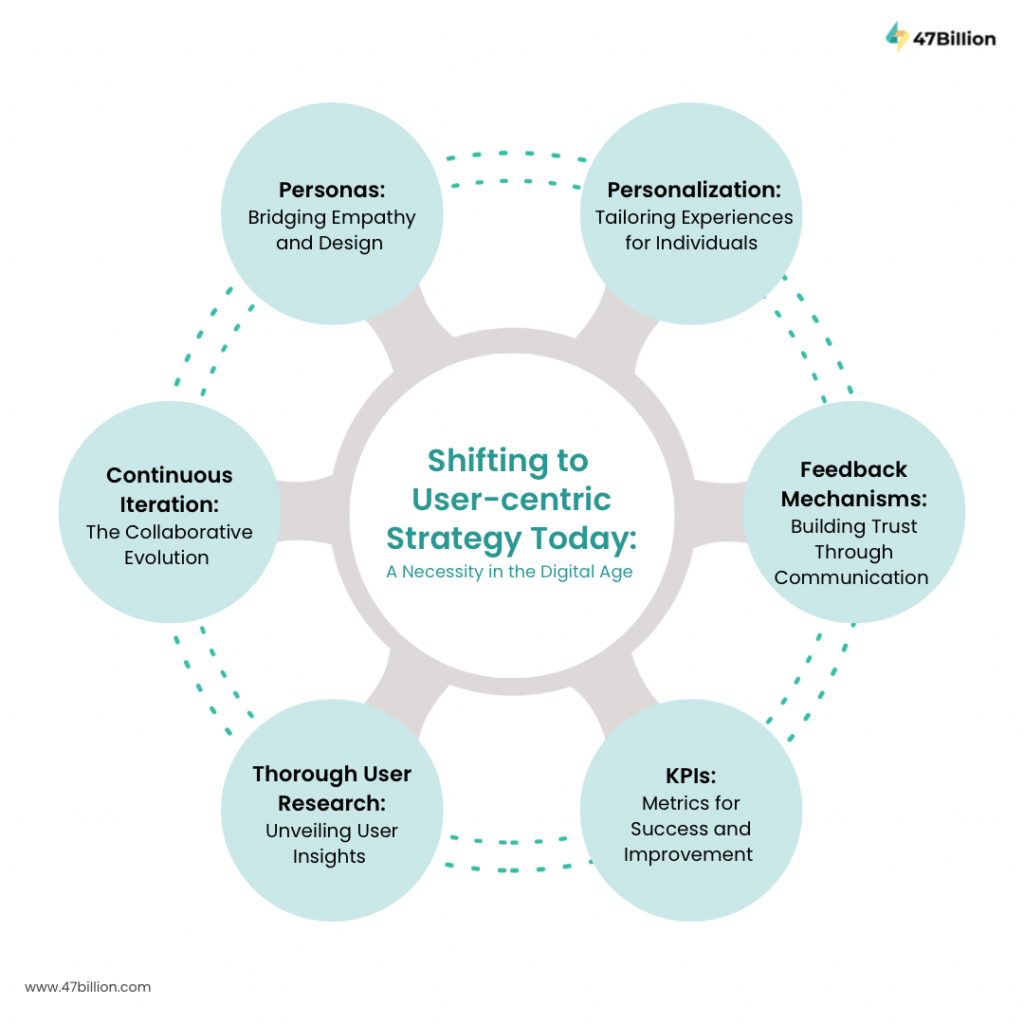
Shifting to User-centric Strategy Today: A Necessity in the Digital Age
In today’s digital landscape, a user-focused strategy isn’t merely an option—it’s a fundamental necessity. Businesses that prioritize understanding, empathizing with, and meeting the needs of their users are better positioned to thrive. Here’s a detailed exploration of the critical components of a solid user-focused strategy:
Thorough User Research: Unveiling User Insights
User research forms the foundation of a user-focused strategy, encompassing both quantitative and qualitative data sources. This involves engaging users through interviews for in-depth insights, collecting structured data via surveys to quantify preferences, conducting usability testing to observe interactions and identify pain points, and utilizing data analytics tools for meaningful pattern analysis. The synthesis of these research methods enables businesses to construct a nuanced understanding of users, providing a solid foundation for informed and effective design choices.
Personas: Bridging Empathy and Design
User personas are more than hypothetical constructs; they’re practical tools rooted in data-driven insights, vital for instilling empathy within design teams. Creating these personas involves developing data-driven profiles ensuring accuracy through information gleaned from user research. By using personas to humanize the design process, designers connect with archetypal users, understanding their goals, pain points, and preferences. This connection facilitates informed decision-making throughout the design process, aligning choices with the specific needs and expectations of the intended user demographic.
Continuous Iteration: The Collaborative Evolution
A successful user-focused strategy hinges on continuous improvement through collaborative efforts between designers and developers. Establishing regular feedback loops allows users to contribute insights, suggestions, and critiques, maintaining an ongoing dialogue that keeps the design responsive to their needs. Embracing agile development methodologies facilitates quick iterations based on user feedback, accommodating evolving user expectations and market conditions. Fostering cross-functional collaboration ensures that insights from user research seamlessly translate into tangible design improvements, creating a dynamic and user-centric digital product.
Personalization: Tailoring Experiences for Individuals
Data-driven personalization is a fundamental element of contemporary user-focused strategies. This approach involves tailoring user experiences based on individual preferences, behavior, and demographic data. Behavioral personalization adapts the user experience to observed behavior, offering recommended content and personalized interfaces. Demographic personalization tailors the interface to align with specific audience segments. Additionally, preference-based personalization allows users to set preferences, providing a sense of control. Through these methods, businesses can significantly boost user satisfaction, engagement, and conversions by delivering personalized experiences aligned with individual preferences.
Feedback Mechanisms: Building Trust Through Communication
Incorporating effective feedback mechanisms is pivotal in a user-centric strategy. This involves creating accessible and seamless user-friendly feedback forms, encouraging detailed insights and issue reporting. Implementing rating systems offers swift, quantifiable feedback, providing a snapshot of user satisfaction. Additionally, direct contact channels like chat support establish a direct line, swiftly resolving issues while showcasing a dedicated commitment to user contentment.
KPIs: Metrics for Success and Improvement
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) act as the guiding metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of a user-focused strategy. Analyzing conversion rates measures the design’s success in turning visitors into customers or achieving desired actions. User retention assesses the sustained appeal and usability of the digital product while monitoring bounce rates provides insights into potential user experience issues. Implementing user satisfaction surveys helps gauge overall happiness, enabling businesses to make informed decisions for continuous refinement by regularly assessing these KPIs.
Conclusion: Pioneering the Future of User Experience
In dismantling the constraints of traditional UX design, the journey toward data-driven user experience emerges as a vital progression, addressing core deficiencies in design methodologies of the past. The pivot to data-driven design is not arbitrary but a strategic response to the evolving demands of the digital landscape.
As businesses transition to data-driven design principles, the impact is transformative. Studies reveal an impressive 15% average uptick in conversion rates within the inaugural year. User retention witnessed a substantial 25% improvement, and proactive engagement with user feedback led to a noteworthy 30% reduction in bounce rates. User satisfaction scores register a remarkable 20% ascent, underlining the tangible advantages of data-driven design.
Conclusively, these statistics underscore a paradigm shift. Data-driven design, anchored in empirical evidence and iterative evolution, stands as the bedrock of contemporary UX design. It not only rectifies the inadequacies of traditional approaches but propels digital experiences into an era defined by user-centricity, adaptability, and measurable success. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, embracing data-driven design is not just a strategic choice—it’s imperative for businesses committed to thriving in the dynamic realm of user experience.
