How AI-Powered Code Generation is Transforming Modern DevOps Practices
In the rapidly evolving landscape of software development, DevOps teams face mounting pressure to deliver infrastructure faster, more securely, and with greater consistency. DevOps autocoding—the practice of using artificial intelligence to automatically generate infrastructure code—has emerged as a transformative solution, reducing provisioning time from days to minutes while maintaining enterprise-grade quality.
The DevOps market is experiencing exponential growth, projected to expand from $10.4 billion to $25.5 billion over the next few years, with AI-powered tools like GitHub Copilot now generating 46% of developers’ code. This revolution is reshaping how infrastructure teams work, enabling unprecedented productivity and innovation.
What is DevOps Autocoding?
DevOps autocoding leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to automatically generate infrastructure code, configuration scripts, and deployment pipelines. This approach transforms natural language requirements into production-ready infrastructure definitions, dramatically accelerating the development lifecycle.
Key Components:
• Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Generation: Automatically creating Terraform, CloudFormation, or ARM templates based on requirements
• CI/CD Pipeline Automation: Generating pipeline configurations for Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and Azure DevOps
• Configuration Management: Auto-generating Ansible playbooks, Kubernetes manifests, and Helm charts
• Security Integration (DevSecOps): Embedding automated security scans and compliance checks from the start
Real-World Impact: A Case Study
The Challenge
A modern enterprise project required building complete multi-cloud infrastructure including Amazon EKS clusters, RDS databases, IAM roles, OIDC provider integration, and service deployments like Rancher for cluster management.
The AI-Powered Solution
Using AI coding assistants, the team provided natural language requirements to generate Terraform scripts. The AI tool analyzed requirements, created implementation plans, generated Infrastructure as Code, detected and fixed errors automatically, verified version compatibility, and created deployment artifacts.
The Results
This comprehensive infrastructure setup, which would traditionally require 3-4 days of manual coding, testing, and debugging, was completed in approximately 30-40 minutes—a 95% reduction in development time. The automated approach provided production-ready code, comprehensive documentation, built-in security configurations, and disaster recovery capabilities.
Core DevOps Autocoding Capabilities
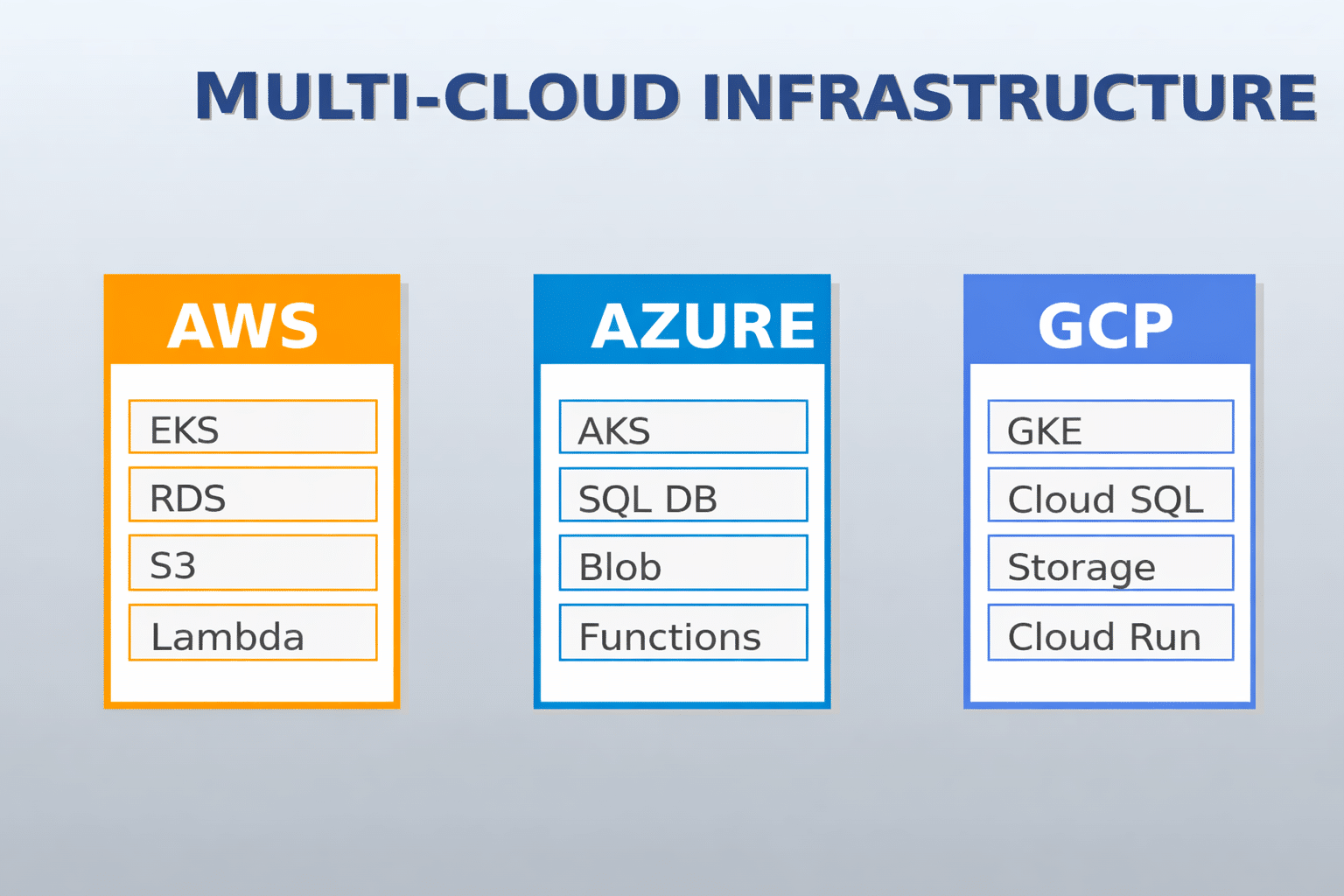
1. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Generation
AI-powered autocoding transforms IaC creation with multi-cloud support across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Modern AI tools generate declarative IaC that describes the desired end state, ensuring idempotent deployments where running the same code multiple times produces consistent results.
2. CI/CD Pipeline Automation
Continuous Integration and Deployment pipelines are essential for modern software delivery. AI autocoding accelerates pipeline creation for GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, Jenkins, Argo Workflows, and Azure DevOps, automatically incorporating enhanced security scanning, optimized caching, and parallel execution.
3. Container Orchestration and Kubernetes
With Kubernetes holding over 32% of the containerization market, AI-powered tools excel at generating deployment manifests, Helm charts, service mesh configurations, and optimized Dockerfiles with multi-stage builds and security best practices.
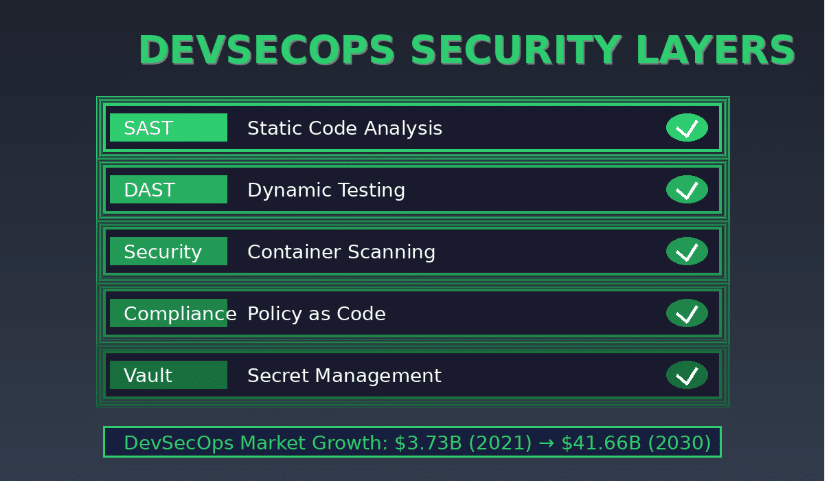
4. DevSecOps Integration
The DevSecOps market is experiencing rapid growth, forecast to expand from $3.73 billion to $41.66 billion over the next decade. AI autocoding embeds security from the start with automated SAST/DAST configurations, container scanning, policy as code, and secret management integrations for HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, and Azure Key Vault.
Best Practices for Implementation
1. Prompt Engineering: Effective DevOps prompts should include specific technology versions, security requirements, networking details, and integration points. Example: ‘Create Terraform for AWS EKS cluster version 1.28 with private subnets, encryption at rest, and CloudWatch logging.’
2. Validation and Testing: Always run terraform validate and plan before applying. Use security scanning tools like tfsec, Checkov, or Terrascan to detect misconfigurations. Run Infracost to estimate expenses and deploy to non-production environments first.
3. Version Control and GitOps: Store all IaC and configurations in Git repositories as the single source of truth. Review AI-generated code through pull request workflows with automated checks, and use ArgoCD or Flux for automatic synchronization.
4. Template Reuse vs. Regeneration: A critical challenge in DevOps autocoding is balancing template reuse against regeneration. While established templates offer production-proven reliability and passed security audits, they face a fundamental problem: Terraform provider versions evolve rapidly, with breaking changes every 6-12 months. A template using AzureRM provider v3.40 from six months ago may fail completely with v4.x due to deprecated syntax, changed resource attributes, and new mandatory fields. Reuse templates when they’re less than 3 months old with current provider versions and changes are purely parametric. Regenerate with AI when templates exceed 6 months, show provider deprecation warnings, or require architectural changes. The optimal approach: maintain golden templates with strict freshness policies (quarterly regeneration using AI), preserve battle-tested architectural decisions in AI prompts, and use automated CI/CD to validate template compatibility with current provider versions.
5. AI Skills and Knowledge Templates (SKILL.md): Advanced AI coding tools support ‘skills’—structured knowledge files (typically SKILL.md) that guide AI behavior to produce consistent, organization-specific outputs. Unlike static code templates, skills teach the AI your standards: naming conventions, security patterns, cost optimization rules, and architectural preferences. For example, a Terraform SKILL.md might specify your resource naming taxonomy (rg-{project}-{env}-{region}), required tags (cost-center, owner, data-classification), approved CIDR ranges, and RBAC policies. When the AI references these skills before generating code, it automatically follows your standards without requiring detailed prompts every time. This approach scales institutional knowledge—capturing senior engineers’ expertise in reusable formats that improve all team members’ outputs. Implement skills by creating domain-specific SKILL.md files for each technology (Terraform, Kubernetes, Azure DevOps), including concrete code examples rather than abstract principles, documenting anti-patterns explicitly, and maintaining version control alongside your infrastructure code. The combination of skills (knowledge) and AI generation (execution) creates a powerful system where templates evolve intelligently while maintaining organizational consistency.
DevOps Autocoding Trends
Agentic AI and Multi-Agent Systems: The rise of autonomous AI systems that can plan, execute, and refine complex tasks without continuous human intervention. Specialized agents for planning, code generation, testing, review, and orchestration work together to deliver complete infrastructure solutions.
Platform Engineering and IDPs: Internal Developer Platforms (IDPs) treat infrastructure as a product, offering self-service provisioning, golden paths with pre-approved templates, and enhanced developer experience through tools like Backstage.
FinOps and Cost Optimization: AI-powered FinOps practices provide automated cost analysis, resource right-sizing recommendations, and waste detection for idle resources and orphaned volumes.
Full-Stack Observability and AIOps: AI for IT Operations transforms monitoring with predictive analytics, anomaly detection, root cause analysis, and intelligent alerting to reduce alert fatigue.
Getting Started with DevOps Autocoding
Step 1: Assess Current State
Audit existing infrastructure, evaluate team skills, identify quick wins, and define success metrics for deployment speed and error rates.
Step 2: Choose the Right Tools
Select AI coding tools based on your technology stack: GitHub Copilot for broad language support, Amazon Q Developer for AWS environments, Gemini Code Assist for Google Cloud, or Claude Code for complex multi-file projects.
Step 3: Start Small and Iterate
Begin with pilot projects on non-critical infrastructure, establish clear review processes, document successful patterns, and measure impact on time savings and deployment frequency.
Step 4: Scale Across Organization
Create template libraries, train teams on AI tools and prompt engineering, implement governance policies, and conduct regular retrospectives for continuous improvement.
Conclusion: The Future is AI-Powered
DevOps autocoding represents a paradigm shift in infrastructure management. By leveraging AI-powered code generation, teams reduce provisioning time from days to minutes while maintaining enterprise-grade quality. With 46% of code now AI-generated and developers completing tasks 55% faster, the transformation is already underway.
However, successful adoption requires more than just tools—it demands cultural change, skill development, and thoughtful implementation. Organizations must balance automation with human oversight, maintain security standards, and invest in training teams for this new paradigm.
The DevOps market’s projected growth underscores the industry’s commitment to automation and efficiency. Companies that embrace AI-powered DevOps autocoding now will gain significant competitive advantages in speed, reliability, and innovation.
The integration of AI into DevOps workflows is no longer optional—it’s essential for organizations seeking to remain competitive in an increasingly fast-paced digital landscape.