Did you know? 83% of consumers believe companies should actively shape ESG best practices, indicating a growing demand for corporate accountability and transparency. Moreover, 86% of employees prefer to work for organizations that align with their values, underscoring the importance of ESG in talent acquisition and retention strategies.
From an investor perspective, companies with robust ESG frameworks are increasingly sought after. ESG investing has been shown to yield higher returns, reflecting growing investor confidence in companies that prioritize sustainability and responsible governance.
Legislative advancements, such as the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), further underscore the importance of ESG reporting. These regulations mandate greater transparency and consistency in disclosing ESG-related information, influencing global corporate governance practices.
Understanding ESG Reporting
ESG reporting involves the systematic tracking, measurement, and disclosure of a company’s performance in environmental, social, and governance realms. Unlike traditional financial reporting, which focuses solely on financial metrics, ESG reporting offers stakeholders comprehensive insights into broader aspects of corporate conduct.
This transparency extends to how companies address their environmental footprint, manage resources, and mitigate climate-related risks. Socially, ESG reporting examines factors such as workforce diversity, labor practices, community engagement, and product safety. Governance aspects cover board composition, executive compensation, ethics, and risk management practices.
By disclosing these non-financial metrics, ESG reporting not only enhances accountability and transparency but also enables stakeholders to evaluate a company’s holistic impact and sustainability efforts. This holistic approach aligns with increasing stakeholder expectations for responsible corporate behavior and sustainable business practices.
Why ESG Reporting Matters?
1. Meeting Stakeholder Expectations: Modern stakeholders, spanning investors, customers, employees, and regulatory bodies, now place a heightened emphasis on transparency and accountability regarding ESG matters. They expect companies to not only meet but exceed minimum compliance standards, seeking robust disclosures that demonstrate proactive management of environmental impacts, social responsibilities, and governance practices.
This shift reflects a broader societal trend towards sustainable and ethical business practices, where stakeholders actively support companies that integrate ESG considerations into their core operations. As a result, ESG reporting serves as a vital tool for companies to build trust, enhance reputation, and align with evolving stakeholder expectations for responsible corporate behavior in a rapidly changing global landscape.
2. Enhancing Corporate Reputation: Prioritizing ESG reporting elevates corporate reputation by demonstrating a commitment to sustainable practices, ethics, and transparency. Companies that embrace ESG principles effectively communicate their dedication to environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and sound governance practices. This proactive stance not only resonates positively with stakeholders but also attracts socially responsible investors seeking long-term sustainability and ethical alignment.
By transparently disclosing ESG initiatives and performance metrics, companies foster trust and credibility. This enhanced reputation strengthens relationships with customers, employees, regulators, and communities. Ultimately, a robust ESG reporting strategy positions companies as leaders in responsible business practices, enhancing their attractiveness to stakeholders who prioritize ethical considerations alongside financial performance.
3. Managing Risks and Opportunities: ESG reporting plays a crucial role in identifying and mitigating risks associated with environmental, social, and governance factors. By systematically tracking and disclosing these metrics, companies can proactively address potential environmental impacts, such as resource depletion and regulatory changes, along with social risks like labor practices and community relations. Moreover, robust governance practices disclosed through ESG reporting enhance transparency and accountability, mitigating risks associated with executive compensation and ethical lapses.
Simultaneously, ESG reporting uncovers new opportunities in emerging sustainability-driven markets. Companies can leverage their commitment to ESG principles to innovate products and services that meet evolving consumer demands for environmentally friendly and socially responsible offerings. This strategic approach not only fosters resilience against external shocks but also positions businesses to capitalize on growing market trends toward sustainability.
Steps to Developing an Effective ESG Reporting Strategy
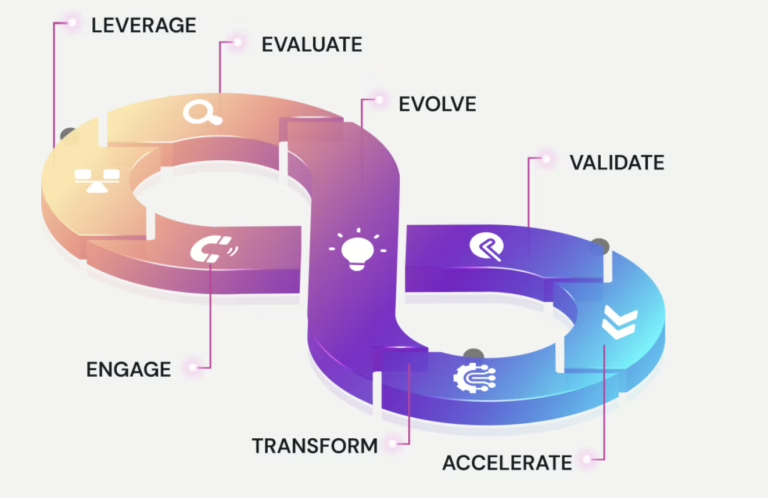
Developing and implementing an effective Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting strategy is crucial for modern businesses committed to sustainability and responsible corporate practices. This strategy not only enhances transparency but also aligns with stakeholder expectations and regulatory requirements. Here are seven essential steps to guide your organization in establishing a robust ESG reporting framework:
1. Define Strategic Objectives
Begin by aligning your ESG objectives with your company’s overarching mission, values, and strategic priorities. Conduct materiality assessments to identify and prioritize ESG issues that are most relevant to your industry, stakeholders, and business operations. This process ensures that your ESG strategy focuses on areas where your actions can have the most significant impact, both internally and externally.
2. Select Appropriate Reporting Frameworks
Choose ESG reporting frameworks that best align with your strategic objectives and industry standards. Popular frameworks include the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). Selecting a suitable framework enables consistent measurement, reporting, and comparison of ESG performance metrics, enhancing credibility and transparency in your disclosures.
3. Integrate ESG into Corporate Governance
Embed ESG considerations into your corporate governance structures and decision-making processes. Assign accountability for ESG performance to senior executives or board members who oversee sustainability initiatives. Establish clear reporting lines and integrate ESG metrics into regular board meetings and strategic discussions to ensure alignment with overall corporate goals.
4. Implement Robust Data Management Systems
Invest in advanced data collection, management, and reporting systems tailored to ESG metrics. Ensure data integrity, accuracy, and consistency across all operations and supply chains. This step is critical for gathering reliable data on environmental impacts (e.g., energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions), social factors (e.g., workforce diversity, community engagement), and governance practices (e.g., board composition, executive compensation).
5. Engage Stakeholders Effectively
Engage with key stakeholders—including investors, employees, customers, and communities—to understand their expectations and concerns regarding ESG issues. Foster transparent communication through regular ESG reports, stakeholder dialogues, and dedicated feedback channels. Incorporate stakeholder input into your ESG strategy to ensure it reflects broader societal and environmental goals.
6. Monitor, Measure, and Report Progress
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and targets to monitor ESG performance and track progress over time. Measure the impact of your ESG initiatives against these KPIs, identifying successes, challenges, and areas for improvement. Prepare comprehensive ESG reports that provide insights into achievements, setbacks, and future strategies, demonstrating your commitment to continuous improvement and accountability.
7. Drive Continuous Improvement
Promote a culture of continuous improvement by learning from ESG reporting outcomes, stakeholder feedback, and industry best practices. Adapt your ESG strategies in response to evolving regulatory requirements, market dynamics, and stakeholder expectations. Incorporate lessons learned into future ESG initiatives to enhance effectiveness, mitigate risks, and capitalize on emerging opportunities in sustainability-driven markets.
By following these 7 steps, organizations can develop a robust and effective ESG reporting strategy that not only meets regulatory obligations but also enhances corporate reputation, stakeholder trust, and long-term sustainability. Embracing ESG principles as integral to business strategy fosters resilience, innovation, and competitive advantage in an increasingly ESG-focused global economy.
Conclusion
Implementing a comprehensive ESG reporting strategy is no longer just a regulatory requirement but a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s complex landscape. By defining clear objectives aligned with corporate values, selecting appropriate reporting frameworks, and integrating ESG into governance structures, companies can enhance transparency and accountability. Solid data management systems ensure accuracy in measuring environmental impacts, social initiatives, and governance practices, while effective stakeholder engagement builds trust and drives continuous improvement.
Monitoring progress through measurable KPIs and regularly reporting results not only demonstrates commitment to sustainability but also positions organizations as leaders in responsible business practices. Embracing ESG principles not only mitigates risks and identifies opportunities but also strengthens resilience and competitiveness in an increasingly ESG-focused marketplace. Ultimately, effective ESG reporting fosters long-term value creation, stakeholder satisfaction, and sustainable growth.