A 30,000 square-meter farm with stacked shelves is all set to produce more than 900 tons of leafy greens annually- from spinach to arugula. It uses around 95% less water as compared to field farming.
The facility is named ECO1. It has been developed in a collaboration between Crop One Holdings and Emirates Flight Catering and is now known as the world’s largest vertical farm.
Emirates passengers are served the produce from ECO1 from July 2022, while UAE residents can buy the greens from stores. They are completely fresh greens that require no testing or washing as they are grown without pesticides or chemicals.
The mission is to cultivate a sustainable future that meets the global demand for fresh, local food, and this farm manifests this commitment. UAE’s new facility is another step towards the UN’s sustainable development goals.
United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization portends alarming statistics that say – the amount of arable land will decrease to only one-third of the amount available in 1970. As climate changes are expected to increase drastically over the next few decades, more intensifying heat stress, droughts, and damage to ecosystems will further hinder our ability to grow crops to feed the billions of people on our planet.
Thus, several economies are shifting to a more innovative vertical farming approach. This method utilizes less than one percent of conventional agriculture’s land and consumes one percent of the amount of water. The alternative has the potential to improve food production along with reducing the environmental footprint of the agriculture sector by reducing land, water, chemical, and fertilizer usage.
The Concept
Vertical farms are a type of controlled environment agriculture. The concept traditionally came from the greenhouses, which have contributed significantly to the global food supply chain during the last decades.
Vertical farming is simply a stack of greenhouses at the top. This method involves growing plants on vertically inclined surfaces or vertically stacked layers. Here, the plants grow in a digitally controlled ecosystem. The system is based on artificial photosynthesis, vertical and zone-wise crop production, and the Internet of Things. Through all the sensor networks, the environmental parameters can be monitored. The retrieved data is displayed on a customized webpage accessible through a digital portal. (A web app or mobile app).
Vertical farms are mainly differentiated based on technological methods used to grow the plants –
Hydroponics: This methodology is used to grow plants on a neutral and inert substrate such as sand, clay, and rock regularly irrigated by a liquid fortified with minerals and nutrients necessary for plant growth. Hydroponic systems use 60-70% less water than traditional farming methods.
Aeroponics: The method involves growing plants in a closed container where plant roots are exposed to a fine mist of nutrient-laden water, regularly sprayed with a nozzle. This method is majorly employed by commercial vertical farms such as Aerofarms and Tower Garden in the US.
Aquaponics: The hybrid method that integrates fish production into hydroponic growing schemes. It used fish waste as a nutrient source for the plants after treatment, operating as a closed-loop system for indoor farming.

Introduction to Vertical Farms
The vertical farming structures rely on a framework that supports integrating various hardware devices and data collection processes, analytics, and automated control of environmental factors through IoT devices situated within the farm. The success of day-to-day operations depends on effective data collection and analysis, which require crop-specific simulation models so that with minimum human intervention, optimal conditions for plant growth can be maintained in the farms.
Digital Framework
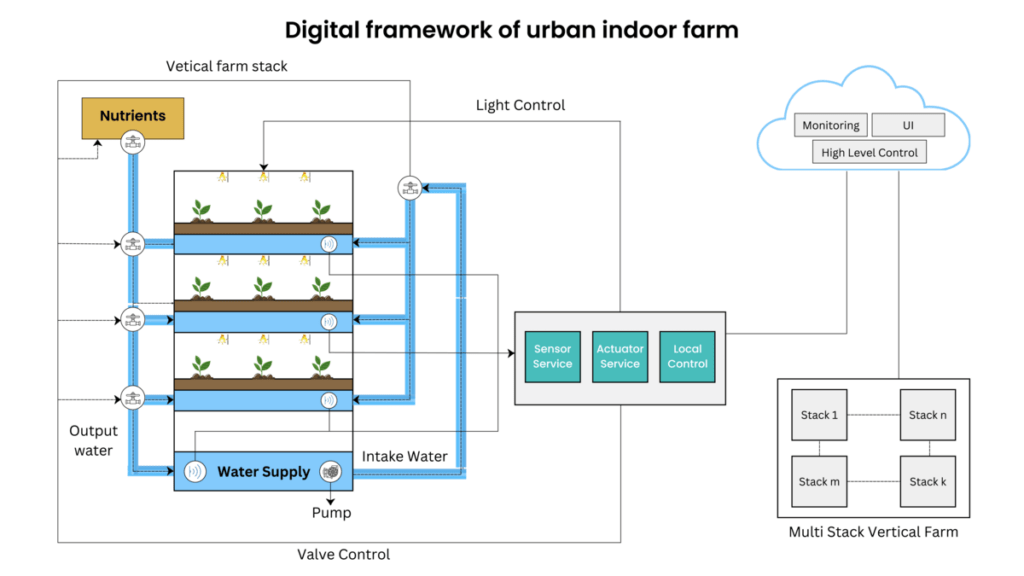
The IoT-based digital framework is an ecosystem with multiple interconnected sub-systems, including the physical, network, middleware, service, analytics, and user experience layers.
Physical Layer – It consists of all the IoT devices, such as sensors, actuators, controllers, switches, network gateways, and routers. The controller is an essential part of this layer which helps data accumulation and transfer to the network modules.
Network Layers – It is responsible for transferring root-level data collected from sensors. It facilitates smart cultivation by transferring specific information required for plant growth to the application layer. The layer consists of various wired and remote interfaces for associating the weeding machine, food harvester, and correspondence of machines and sensors with cloud frameworks.
Middleware Layer – it has the essential function of boosting IoT security. It acts as device controlling, settling management, sensation, platform ability, and surveillance relevant tasks. Middleware remains in the middle of the utilization and network layers, which can handle information. It helps in storing data and data transfer over the wireless module.
This layer is for sensor information procurement, materials recognition, crop health condition data monitoring, and factual investigation administrations are cleared to encourage the detecting, activating, and infection recognition operation.
Analytics Layer – It aims at controlling major crop growth KPIs to predict what crops can provide better advantages and returns.
The user experience layer includes a user-friendly, real-time monitoring dashboard with an enhanced, consistent UI. It involved functions like nutrient management, irrigation management, light management, and growth zone management for optimum plant growth.
How vertical farming ecosystem is revolutionizing the scenario?
Vertical farms are making a momentous impact on traditional agriculture practices –
Sustainable Irrigation
Irrigation has to be the most efficient practice in agriculture. With the advancement of vertical farming, growers can rely on complex irrigation systems that accurately monitor the moisture in the vertical stacks and deliver water in a proper schedule with consistent quantity as per the requirement of the particular crop. This helps prevent water wastage and maintain plant health with appropriate watering patterns.
Intelligent Sensing for Effective VPD Control
VPD here stands for vapor deficit. When VPD is low, environmental stress is insufficient for effective transpiration and uptake of nutrients from the root. When it is high, the water vapor level in the atmosphere gets to a lower value. Thus the optimum value of VPD is required by plants to flourish. The smart sensing tech can monitor significant factors related to calculating VPD, such as relative humidity, the surrounding temperature, the leaf temperature, etc., and adjust accordingly. This allows vertical farm managers to achieve a perfect environment without human intervention.
Effective Nutrient Recipes for Crops
These advanced farms help constantly monitor and adjust the nutrients fed to the plants. The data-driven systems allow farm managers to generate high yields by maintaining balanced nutrient mixture ratios, light radiations, and carbon dioxide levels. This helps in harvesting products of better quality with fewer resources.
Clean Environment for apt crop growth
Pests have been creating challenges for farmers in traditional agricultural practices. But AI-induced vertical farming helps farm managers act defensive against bugs. The AI-based models help farm managers with real-time information about insects and methods that can be used to descend their impact in the closed indoor farm environment.
Towards a Sustainable Future
Technological advancements are making agriculture practices more accurate. It helps guide farm managers about optimum planting, water management, crop rotation, timely harvesting, and nutrient management. Predictive analytics helps maintain appropriate growth conditions, measure crop sustainability, and evaluate farms for the presence of diseases, pests, and poor plant nutrition. Utilizing the KPIs such as VPD, temperature, precipitations, and air and light radiations for effective plant growth has changed agriculture practices. Vertical farming has the potential to increase food production along with effectively managing the environmental footprint of the agriculture sector by reducing land, water, chemical, and fertilizer usage along with decreasing human intervention.
47Billion is glad to announce an enhanced business strategy formulated to maximize the combined impact of its technologies, solutions, and capabilities to address some of the biggest global challenges and support the UN Sustainability Development Goals.
How do we enable this? Click here – 47Billion Is Taking UN Sustainability Goals To The Next Level Of Impact